Chongqing – The New Frontier for Foreign Investment in Southwest China
We take a look at the factors that make Chongqing an attractive investment destination for foreign firms in Southwest China.
In a year where China overtook the United States as the main destination for foreign investment, the diversification of that investment within China has been dynamic and cities that were once not the primary target are now on the radar of international companies.
I speak of Chengdu and Chongqing, the two largest and richest cities in western China. Chongqing is an independent municipality under the central government administration and Chengdu is the capital of the province of Sichuan. Both cities feature in the top 10 of richest cities in all of China; Chongqing is ranked fifth and Chengdu seventh.
The region’s favorable appeal for investment has been known for quite some time. However, since the past few years, membership to foreign chambers of commerce has been growing, more events and activities are being organized by these institutions, and the foreign business and expatriate community is growing at large.
Of course, there is a reason for this surge in growth. The governments of both Chengdu and Chongqing, following the example of governments in other mega Chinese cities, have been enacting friendly policies to attract foreign investment to the region and so far, the effort is paying off.
In this article, I will be focusing on Chongqing and considerations that make it attractive to locate your investment here. This will be followed up by a spotlight on Chengdu in a subsequent article.
Locating your investment in Chongqing
Focusing on Chongqing, this city is one of the four municipalities under the direct administration of the Chinese central government (the other three are Beijing, Shanghai and Tianjin), and the only such municipality located deep inland. The municipality of Chongqing, roughly the size of Austria, includes the city itself, as well as various adjacent cities.
What is however worth knowing is the key areas where foreign companies have set up here and their relative advantages.
Yuzhong District
Dubbed “old town” by the locals, Yuzhong is the central district and capital of Chongqing municipality. It is also the political, economic, and entertainment center of the city. Located in the central portion of Yuzhong is the Jiefangbei central business district, a leading business and financial center of western China.
This is the natural choice of place for setting up any operation focusing on retail or services; in 2020, wholesale and retail sales in the bustling center increased by 8.3 percent and 5.8 percent, respectively, year-on-year, according to the Chongqing Municipal Commission of Commerce.
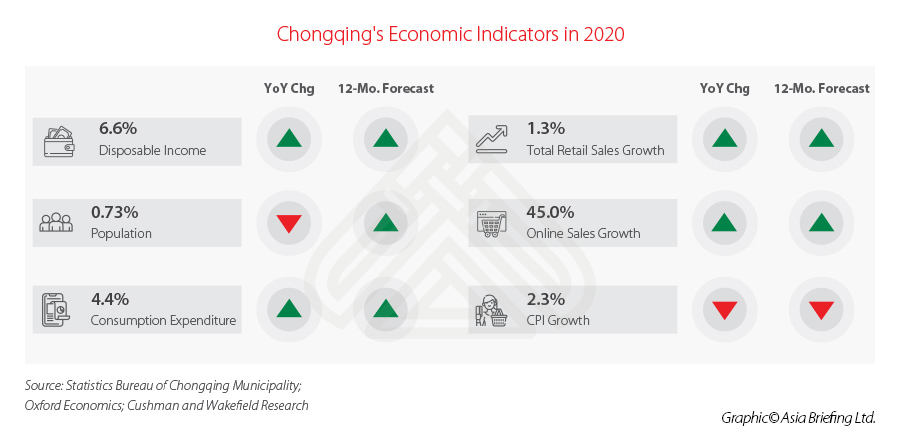
In fact, total retail sales of consumer goods increased by 1.3 percent to reach RMB 1.7872 trillion (about US$277 billion), second only to Beijing and Shanghai. The growth rate was higher than the national average of 5.2 percentage points, ranking 4th in China.
Also, important economic indicators, such as disposable income, population, and consumption expenditure are on the rise, and e-commerce is growing at a rapid rate – which is also reflected in the national trend.
Liangjiang New Area
Chongqing’s Liangjiang New Area (“LNA”) was set up with the approval of the State Council on June 16, 2010, the 13th anniversary since Chongqing became China’s fourth municipality. Located in the main urban districts of Chongqing, north of the Yangtze River and east of the Jialing River, LNA covers 1,200 square kilometers, of which 550 sq. km. is available for construction and composed of Jiangbei, Yubei, and Beibei administrative districts, the North New Zone, and China’s first inland bonded zone, Lianglu Cuntan Bonded Port Area. Chongqing LN Development & Investment Group Co., Ltd. oversees construction of the industrial parks.
Similar to Shanghai’s Pudong region, which in the 1990s was a desert but is now the financial center of the city after years of domestic and foreign investment, Chongqing’s Liangjiang New Area is attracting considerable investment. The LNA especially welcomes foreign investment in prospecting and mining of non-oil/gas mineral resources. Foreign investors are permitted to establish sole proprietorship or to cooperate with Chinese counterparts in risk exploration of non-oil/gas mineral resources. They are also permitted to purchase prospecting and mining rights of non-oil/gas mineral resources from large and medium-sized state-owned enterprises and can also transfer these rights.
Also, worth knowing is the fact that LNA’s local government is quite proactive in making sure that the area is a target for foreign invested companies, particularly in the manufacturing sector, and has started to establish deals with representatives of foreign governments, such as chambers of commerce, who act as the go-between between the local government and the companies of their own countries (for example, the Italian Chamber of Commerce in Chongqing is located in the LNA).
Naturally, companies that invest in this area can enjoy many subsidies and benefits, which are all negotiable with the local governments, depending on the size and expenditure of the project.
Other areas and special economic zones
Other than the two areas mentioned above, Chongqing has many other locations which may attract foreign interest, namely:
Chongqing Pilot Free Trade Zone
Established on March 15, 2017, with an area of 119.98 square kilometers, covering the LNA, Xiyong area, and Guyuan port area.
It focuses on the development of manufacturing of high-end, digital, or intelligent equipment, cloud computing, biomedicine, and services, such as international transit and integrated distribution.
In 2020, 14,393 enterprises were newly established in Chongqing Pilot FTZ, with registration capital totaling RMB 140.97 billion (US$21.71 billion). Among them, 129 are foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs), with a total registration capital of US$843 million.
Chongqing high-tech industrial development zone
Chongqing High-tech Industrial Development Zone, approved in March 1991, has a total planning area of 1,093 square kilometers, focusing on the development of biological drugs, precision medical and other large health industries, power semiconductors, the internet and other new information technology industries, automobile electronics, intelligent robots, and other advanced manufacturing industries, testing certification, R&D services, and other high-end services.
Chongqing economic and technological development zone
Chongqing Economic and Technological Development Zone was established in 1993, with a total area of 90 square kilometers. The economic development zone has formed the industrial foundation of electronic information, high-end equipment manufacturing, modern service industry, and other industries.
Business registration
New companies may be established by joint venture or reinvestment from foreign-invested enterprises and domestic enterprises and can enjoy benefits as foreign-invested enterprises if the proportion of foreign investment reaches or surpasses 25 percent.
For foreign investors that appraise their high and new technologies for registered capital, the appraised value can surpass 20 percent of the registered capital.
Tax
- Corporate income tax rate of 24 percent applies to manufacturing foreign-invested enterprises.
- Enterprises that have been operating for 10 years or more are exempt from corporate income tax for two years, following the enterprise’s first profitable year. From the third to the fifth year onwards, the corporate income tax rate is 12 percent.
- Corporate income tax rate of 15 percent applies to foreign-invested enterprises engaged in technology- or knowledge-intensive projects, or with an investment of over US$30 million and on a long-term operation basis, or engaged in energy, transportation and harbor construction projects.
- Corporate income tax rate of 15 percent applies to foreign-invested enterprises covered in the Encouraged category and Restricted Category B in the Catalogue for Guidance of Foreign Investment Industries.
- Corporate income tax rate of 15 percent applies to productive foreign-invested enterprises in the Chongqing Economic and Technological Development Zone, Chongqing High and New Technology Industry Development Zone and Chongqing North New Zone. Foreign-invested high and new technology enterprises that have been operating for 10 years or more are exempt from corporate income tax for two years following the enterprise’s first profitable year.
Costs of doing business
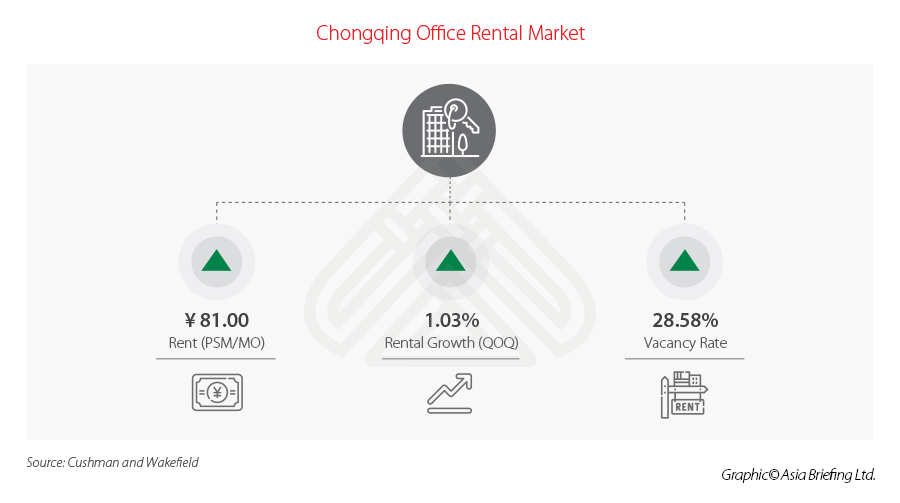
Overall, as of 2021, in Chongqing the average price of an office is RMB 81 per square meter (rental), roughly US$12.5, which puts the city in a highly competitive position, when comparing it to other metropolises in China.
In addition to this, and speaking from personal experience, it Is not uncommon to get offers in premium office towers and venues of an amount equal to RMB 2,000 / month for a small office for two to three people, with everything included. Such offers are explainable, due in part to the city’s still high vacancy rate, considering that construction is on the rise and the supply is higher than the demand.
Finally, and should you be eligible for preferential treatment by local officials (in China, each city has districts, and each district is managed independently), then you may be granted free rental space, as well as other benefit. These are at the discretion of the local administration and can be arbitrarily decided.
Also, in what concerns average salaries, as of 2020, the average annual salary for employees working in non-private owned companies (which according to Chinese statistics includes state-owned companies, foreign and Hong Kong / Macao / Taiwan invested companies) was RMB 89,714, which translates into roughly RMB 7,500 a month or US$1,159 dollars.
This also shows how much the region has grown in terms of productivity and income growth, which has an impact on talent pool, consumption, and market opportunities, when compared to what the figure was in 1996 – RMB 5,010 or US$774 dollars, annually.
Takeaways
Speaking from personal experience and after assessing the region on the ground, Chongqing seems to be at the stage that other cities like Shanghai or Beijing were in the early 2000s, when foreign companies and investment did not abound as much as they do today.
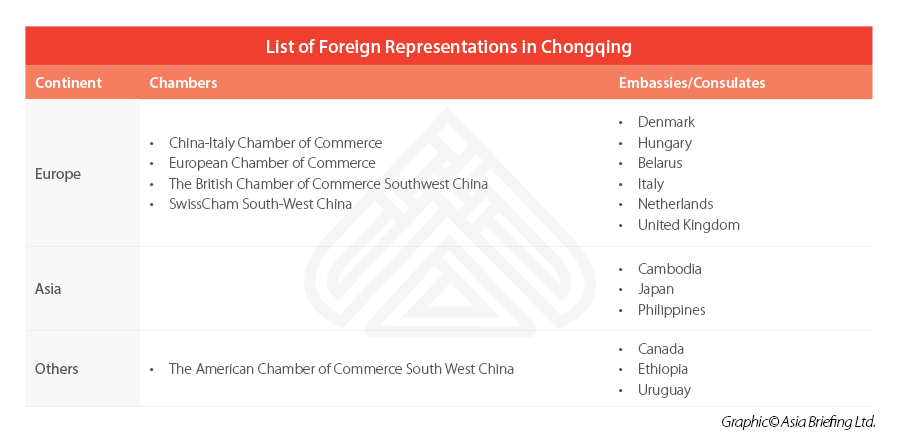
However, as things tend to move quickly in China, many countries have already planted their flag here and established either a consulate or a chamber of commerce (or sometimes both) and the region is already a focus for foreign investment, which is still on the rise.
As this tendency will only increase, the time is ripe now, when costs are relatively low, due to low average salaries (as pointed out above) and general cost of live. Added to this is the eagerness of the local governments to have foreign investors is high and no opportunities still abound.
Related Reading
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article Digital Expense Management in China: How Big of a Deal is it?
- Next Article Revisione obbligatoria dello statuto delle Joint Venture sino-italiane: è iniziato il conto alla rovescia