Establishing a Branch Office in Beijing: Stay Compliant with the New Social Insurance Policy
On June 30, 2020, the Beijing Social Insurance Fund Management Centre issued the Notice Regarding Several Issues on Participation of Labour Dispatch Companies and Human Recourses Service Companies in Social Insurance Scheme (“Notice”) – enforceable from September 2020, which marks the end of the grace period.
The main consequence of this Notice is that labor dispatch companies and human resources companies (“HR agencies”) will not be allowed to be engaged by companies that are not registered in Beijing, in order to pay the social insurance on their behalf for their Beijing based-staff.
What are the implications of the new social insurance compliance obligation?
According to the Notice, Beijing HR agencies are required to declare the real employer’s unified social credit code (organization code) in the online social insurance system when opening insurance accounts or transferring the social insurance relationship for labor dispatch employees and labor outsourcing employees. And, if the real employer’s unified social credit code does not match any registered entity in Beijing, the system will not be able to process the request.
Hence, the common practice of entrusting a local third-party HR agency to deal with the social insurance obligations in Beijing on behalf of a company registered somewhere else in China – will not be allowed anymore – and all the enterprises not registered in Beijing have to take the necessary measures to be compliant with the new policy.
Companies that fail to comply with the Notice shall be incapable of paying local social insurance contributions for their Beijing employees, which will lead to potential government penalties and labor disputes.
What are the options available to companies not registered in Beijing?
In the light of above, enterprises not registered in Beijing may either adopt employment structuring solutions, or – what is recommended – should establish an entity (a subsidiary or a branch) within the city to process social insurance withholding and execute the payment, or entrust an intermediary HR agency to withhold and pay employees’ social insurance on their behalf after they obtain business license and open social insurance and housing provident fund accounts in Beijing.
Subject to limitations, some business entities may use dispatch or other forms of employment structuring – but the rules are different and companies will need to understand how they apply to their respective structures (representative office or wholly foreign-owned enterprise) – or they will be found incompliant and/or penalized.
Further, while an employment structuring solution is cheaper and more flexible, “it can only serve as a makeshift solution, which cannot rectify the incompliance permanently,” according to Fanny Zhang, Business Advisory Services Manager at Dezan Shira and Associates’ Beijing office. Besides, it may trigger future labor dispute risks where companies and employees cannot reach a consensus on such arrangements.
For companies that want to achieve full compliance and avoid any potential risks, setting up an entity in Beijing is a more suitable solution, though the management cost is relatively high for the employee. The company can either set up a subsidiary or a branch office under this option. A representative office is not a feasible option here because it is not a legal entity and cannot hire personnel directly in Beijing.
While a subsidiary is an independent legal entity – separated from the parent company, bearing its own civil liabilities and conducting its own business operations regardless from those performed by the parent company – its establishment implies a duplication of structure costs and capital injection requirements.
A branch office is simply an extension of the parent company outside of its residence, carrying out only the activities performed by the parent company with the parent company bearing all the liabilities.
The branch office can enter into employment agreements locally, register on the Beijing Municipal Human Resources and Social Security Bureau self-service platform, and comply with the social insurance obligations – without entailing elevated costs. In fact, the cost and management of a branch office is rather low and easier as compared with that of a subsidiary entity.
Besides, the time-frame of setting up a branch in Beijing is about four to five weeks, including opening a social insurance account; this is much faster than setting up a subsidiary.
To summarize, setting up a branch office bears the below advantages among all the options available:
- Fully compliant with the current law and regulations in Beijing, no potential risks under this option (as compared to employment restructuring solutions);
- Will not be challenged by the local Administration of Market Regulation and the Tax Bureau (as compared to employment restructuring solutions);
- Allows the employer to apply for “Beijing working residence permit” (工作居住证) for employee who has no Beijing hukou and is hired by a branch office (unlike employment restructuring solutions);
- Can sponsor working visa for expat employee (unlike employment restructuring solutions);
- Easier to set up – the time-frame of setting up a branch in Beijing is about 4-5 weeks, including starting a social insurance account (when compared to setting up a subsidiary); and
- Relatively low in management cost (as compared to setting up a subsidiary).
The preferred option: Set-up a branch office in Beijing
Based on the above assessment, the best solution to comply with the requirements stated under the Notice, is setting up a branch, which will work as an extension of the parent company, without being independent from it, neither legally nor financially.
Below we present the general guidance for setting up a branch office in Beijing.
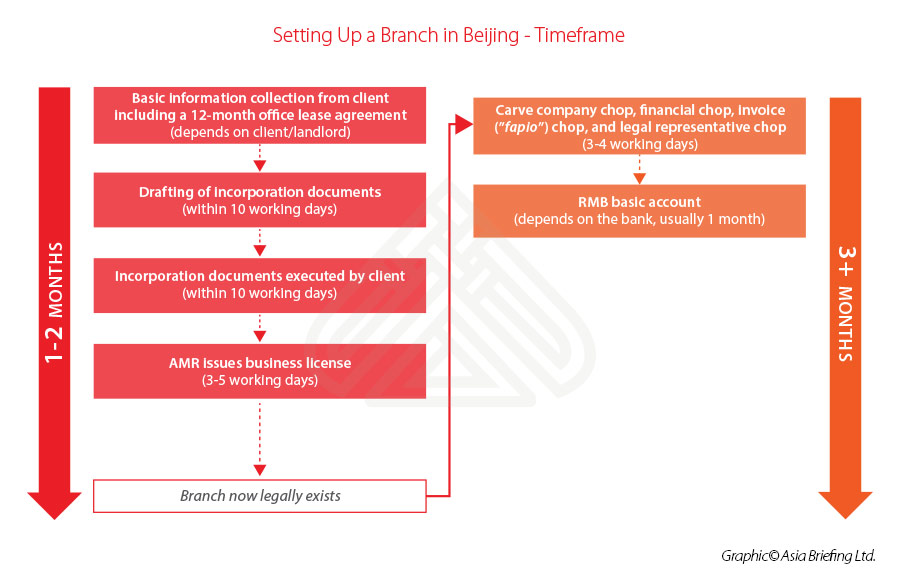
It should be noted that although the establishing procedure of a branch office is quite straightforward, the detailed requirements and procedures may still vary from one district to another. (Generally, it takes about four to five weeks to set up, including open a social insurance account, and approximately three months if we take post-registration activities into account.) Companies are suggested to consult with professional services firms for efficient and smoother transition.
What are the preparatory documents?
The set-up of a branch office in Beijing requires the following documents:
- Name of the branch, which should consist of the parent company name + branch location + Chinese word for “branch” (分公司);
- Identification document of the person in charge of managing the day-to-day operations of the branch;
- Identification document of the person in charge of the company finance, for example, chief accountant or chief finance officer;
- Incorporation documents of the parent company, including the articles of association and the business license;
- Lease Agreement related to the office where the branch is going to be established;
- Business scope, which will have to include the same activities (all or just or few of them) of the parent company; and
- Bank details for the bank account opening.
Businesses are suggested to pay attention to the formality requirements of different documents to avoid unnecessary back and forth in the later registration procedures. For example, all documents in foreign language are required to be translated into Chinese by authorized translation agencies.
Once the above documents are ready, the branch registration procedure shall start.
Registration procedure
After having collected all the documents needed from the parent company, the registration procedure can be initiated either by filing the documents on-site, or online, via the platform managed by the Beijing Administration for Market Regulation (“BAMR”) website.
Online application
When filing online:
- The person in charge of managing the day-to-day operations and the agent that is entrusted to deal with the registration must register their identification on the platform.
- The agent fills in relevant information on the platform. The platform will automatically verify whether the company name can be used and whether the shareholders are blacklisted.
- Relevant persons give their signature online.
- Upon review, an e-business license will be issued online for download at any time if the materials are complete and correct. The paper business license can be obtained on-site or be delivered by courier service.
On-site application
When the company decides to make business registration on-site, it can submit all required application documents to the BAMR in person.
- Acceptance: If the application documents are complete and correct, the application will be accepted on-site. If the application documents are not complete, the BAMR will issue a notice indicating how to make rectifications.
- Review and approval: Upon review of the application documents, the BAMR will decide whether to approve the application. A written notice will be given if the application is approved or refused.
- Obtaining license: Upon approval, the paper business license can be obtained on-site or be delivered by courier service.
Once the business license is issued, the branch is deemed to be duly established under Chinese laws and technically allowed to operate within its business scope.
Post registration activities
After obtaining the business license, the branch office still needs to go through the following formalities:
- Application for approval at the Public Security Bureau for the carving of the branch chops;
- Tax registration (including fapiao application);
- Opening an RMB basis account at the bank indicated by the parent company; and
- Applying for internet banking facility at the same bank.
At the same time, the registration at the Beijing Municipal Human Resources and Social Security Bureau self-service platform for Employment Insurance registration can be processed.
Under the general background of business reform and facilitation, some of the post-registration activities start to be available for online management gradually. But again, businesses wanting to set up a branch office are suggested to cooperate closely with their service providers on the procedures.
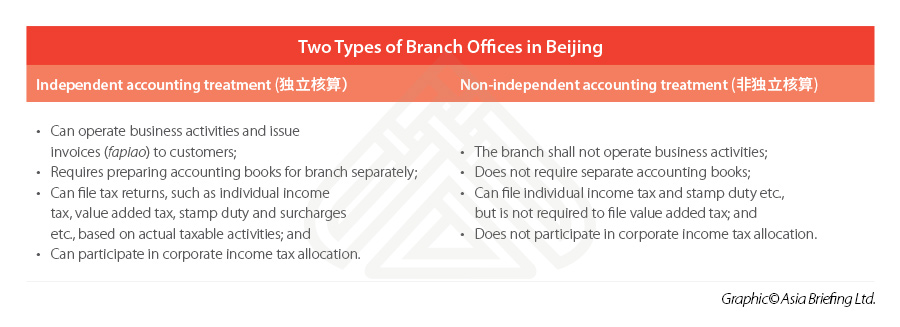
One thing to be noted in the tax registration process is that there are two types of branches that can be registered in China:
- independent accounting treatment branches; or
- non-dependent accounting treatment branches.
The distinction is based on the accounting system and corporate income tax allocation adopted, and therefore on the grade of independence that the branch has with reference to its parent company.
While the non-independent branch does not have its own accounting system and all tax declarations should be submitted by the parent company on a consolidated basis, the independent branch has its own independent accounting system, and it can file its taxes directly with the local tax bureau.
Whether the branch office wants to be identified as an independent accounting treatment branch or non-independent accounting treatment branch, they must clearly describe their business activities and corresponding business scope – when applying to the tax bureau.
The setting up procedure, starting from the preliminary activities until the completion of the post registration activities, can be summarized as follows:
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
We also maintain offices assisting foreign investors in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, United States, and Italy, in addition to our practices in India and Russia and our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative.
- Previous Article China Individual Income Tax and Social Insurance Calculator
- Next Article Erschließung neuer Wachstumschancen auf Chinas F&B-Markt