Investing in Tianjin: China City Spotlight
In this city profile, we discuss the factors that make investing in Tianjin a viable option for international businesses. Tianjin is a manufacturing center and leading port in northern China.
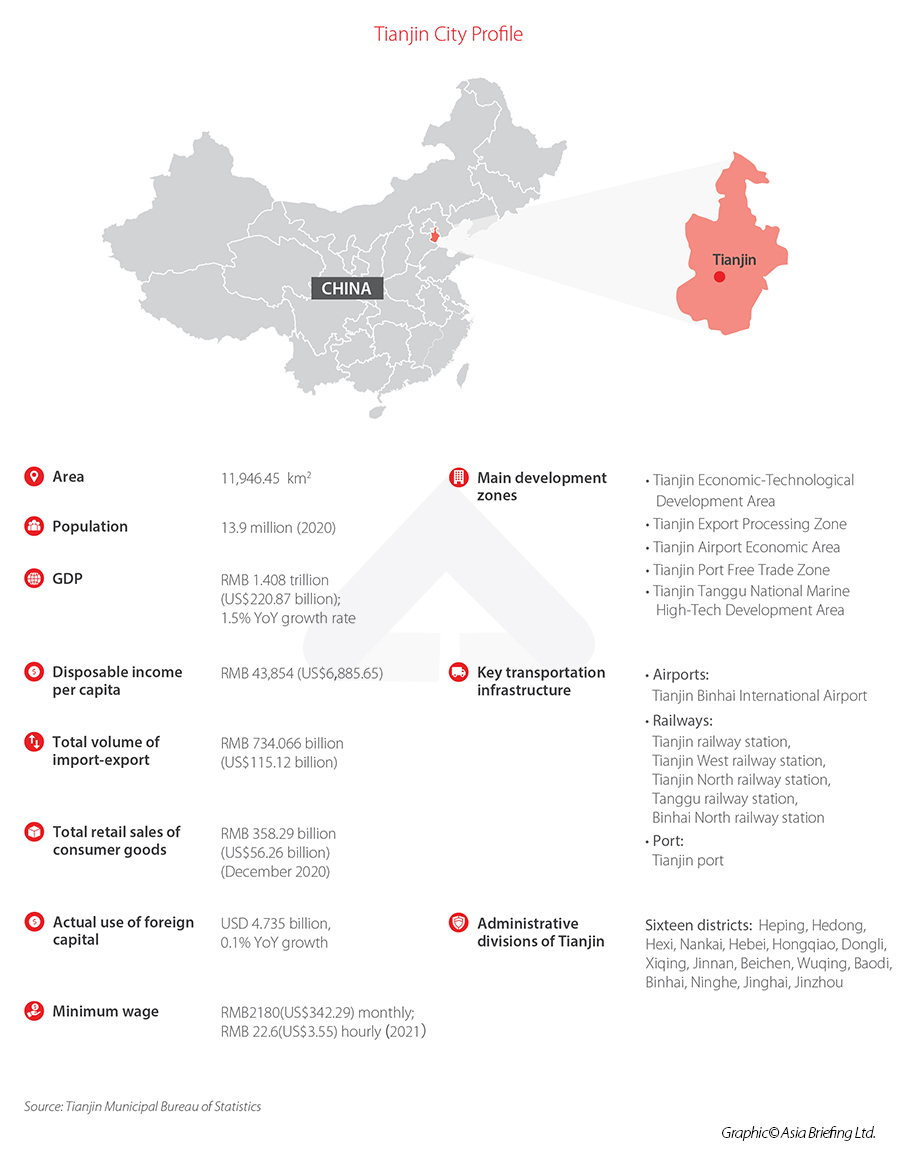
Tianjin is a metropolis on the northeastern coast of Mainland China. It is one of the four autonomous municipalities in the country, along with Beijing, Shanghai, and Chongqing, that are under the direct administration of the central government.
Tianjin borders Hebei Province and Beijing Municipality, bounded to the east by the Bohai Gulf portion of the Yellow Sea. As part of the Bohai Economic Rim, Tianjin is the largest coastal city in northern China and part of the Jing-Jin-Ji megapolis. It is northern China’s most important manufacturing center and leading port.
Tianjin has been included in the world’s top 100 cities and in the Global Financial Centers Index. It is ranked as a Beta (global second-tier) city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network.
Tianjin is among the world’s top 25 cities for scientific research output as tracked by the Nature Index. The city is home to multiple notable institutes of higher education in northern China, including Tianjin University, Nankai University, and Tianjin University of Technology.
Tianjin’s economic profile
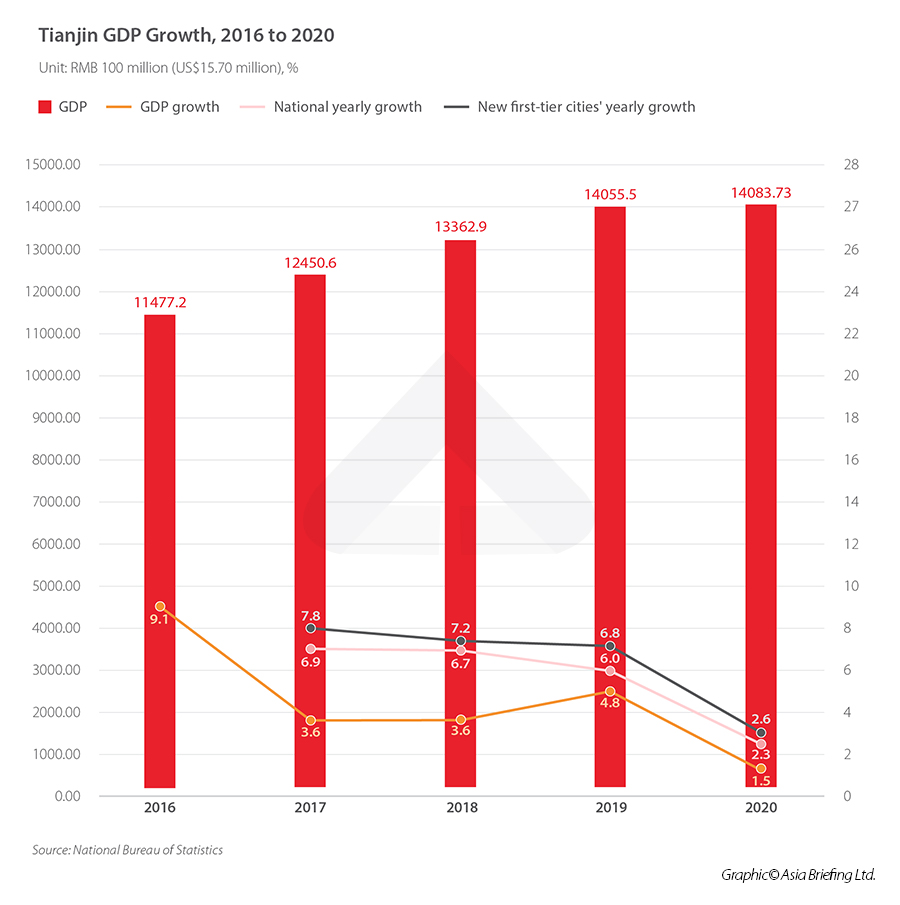
From 2016 to 2020, Tianjin’s GDP continued to grow. In 2020, Tianjin’s GDP ranked eleventh in the country above the average GDP of the ‘new first-tier cities’, which is about RMB 1,408.373 billion (approx.US$220.87 billion). The new first-tier cities refer to the 15 cities that have entered the “2021 City Business Charm Ranking List” published by China Business Weekly – Chengdu, Hangzhou, Chongqing, Xi’an, Suzhou, Wuhan, Nanjing, Tianjin, Zhengzhou, Changsha, Dongguan, Foshan, Ningbo, Qingdao, and Shenyang. The established first-tier cities continue to be Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, and Guangzhou.
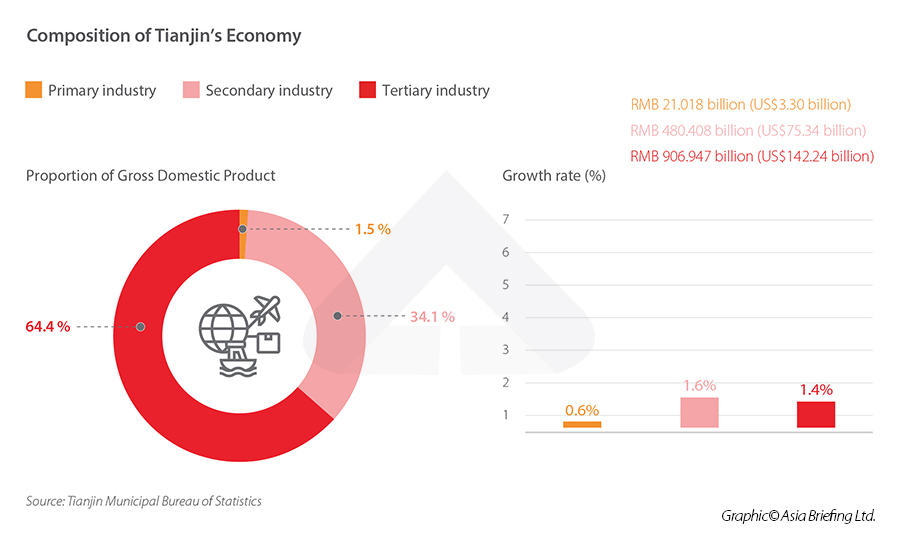
For sector-wise contribution to the GDP in 2020, the city’s primary sector added a value of RMB 21.018 billion (approx.US$3.30 billion), a decrease of 0.6 percent. The secondary sector added a value of RMB 480.408 billion (approx.US$75.34 billion), an increase of 1.6 percent. The tertiary sector added a value of RMB 906.947 billion (approx.US$142.24 billion), an increase of 1.4 percent. Despite the impact of COVID-19 in 2020, the city’s secondary industries expanded for seven consecutive months. During that time, the secondary sector accounted for 72.9 percent of total industrial output among all local businesses with a turnover of more than RMB 20 million (US$3.9 million). The contribution of the primary, secondary, and tertiary industries to GDP growth was 1.5 percent, 34.1 percent, and 64.4 percent, respectively.
To be noted, the year-on-year GDP growth rate of Tianjin has been lower than the national yearly GDP growth rate and the average yearly GDP growth rate of the new first-tier cities since 2017, but the gap was narrower in 2020. In 2020, Tianjin’s GDP growth rate was 1.5 percent yearly, while the national GDP growth rate was 2.3 percent year-on-year. The average year-on-year GDP growth rate of new first-tier cities was 2.6 percent.
The main reason for the gap is that Tianjin is going through a period of transformation. Tianjin’s industrial structure, which used to be dominated by heavy and chemical industries, is being adjusted. The municipal government is endeavoring to develop the advanced manufacturing industry, the high-tech industry, and the modern service industry – to modernize the city’s economic profile. Naturally, the city is eliminating a large quantity of now obsolete production capacity and creating the base to establish new industries. In addition, Tianjin changed its statistical methods in 2016/2017 to improve the data quality.
Despite the low GDP growth rate in general, Tianjin’s high-tech and other emerging industries keep growing. In the first half of 2021, the added value of strategic emerging industries increased by 23 percent year-on-year, with an average growth of eight percent over the past two years. The added value of high-tech industries (manufacturing) grew by 24.4 percent year-on-year, with an average growth of 8.5 percent over the past two years. By product output, the output of service robots increased by 2.7 times, new energy vehicles by 1.6 times, integrated circuits by 67.6 percent, elevators by 36.8 percent, and industrial robots by 28.9 percent.
Given Tianjin’s strength in R&D and the role it’s being assigned in Outline of the Plan for Coordinated Development for the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region, the city’s advance manufacturing sector is expected to grow further in the foreseeable future.
Foreign trade and investment
In 2020, Tianjin’s total volume of imports and exports reached RMB 734.066 billion (approx.US$115.12 billion) and basically restored to the pre-pandemic level. Among them, exports were RMB 307.512 billion (approx.US$48.23 billion), an increase of 1.9 percent. Major exports include mechanical and electronic products.
As to trading partners, the main export markets were the European Union (EU), the United States (US), South Korea, Japan, and Hong Kong. In 2020, Tianjin’s exports to the EU and the US increased by 3.8 percent and 2.2 percent, respectively.
In 2020, foreign investment promotion in Tianjin achieved positive results. There were 570 newly approved foreign-invested enterprises in Tianjin, with contractual foreign investment of US$36.248 billion, an increase of 14.7 percent, and actual direct use of foreign capital of US$4.735 billion, an increase of 0.1 percent. Tianjin has been widening its opening up through active integration into the “Belt & Road”. Finally, 99 companies were established overseas in 2020 as a result of the outbound direct investment (ODI) promotion.
Planning for the parallel development of “Twin Urban Areas”
The strategy of twin urban areas is through the axial development between the two areas. Important resources are concentrated in identified centers and key regions, which improves the efficiency of land use and avoids the continuous development of areas. Jin area and Bin area are the two key regions identified in Tianjin; Jin area refers to the old town, while Bin area refers to the new town. The new pattern of twin urban areas development coincides with Tianjin’s urban development history of “one shoulder carrying two”. Jin area focuses on the cultural heritage and characteristics of the combination of Chinese and Western and the blending of ancient and modern that developing modern service industries, including finance, culture, tourism, etc. Bin area focuses on combining marine culture and modern industrial culture that develops financial innovation, advanced manufacturing, R&D, and production.
Bin Area: Upgrade from “manufacturing” to “intelligent manufacturing”
Tianjin is the cradle of China’s modern mechanic industry and textile industry, and many products and original inventions in many industries in China were born in Tianjin, such as Flying Pigeon bicycles, Seagull watches, and Beijing brand televisions. At present, Tianjin has all 41 major industrial categories, 191 of the 207 medium categories, and 606 of the 666 sub-categories, making it the city with the most complete industrial system in China.
There is no doubt that the manufacturing industry is the pillar and lifeblood of Tianjin. A transition from the transitional manufacturing industry to emerging industries is underway, relying on the strategy of major industrial projects to optimize the city’s industrial structure. Eight emerging pillar industries have been formed, including aerospace, petrochemical, equipment manufacturing, electronic information, biomedicine, new energy, new materials, and the defense industry.
Tianjin has made the intelligent technology industry a core driving force of its high-quality development. Towards this, Tianjin established a special financial fund of RMB10 billion (approx.US$1.57 billion) for intelligent manufacturing and supported five batches of 1726 projects. Also, the local government arranged funding worth RMB 5.21 billion (approx.US$0.82 billion) for building 102 intelligent factories and digital workshops, such as Haier’s 5G factory and Danfoss. In the first half of 2021, the fifth consecutive World Intelligence Conference was successfully held here, creating a “new business card” for Tianjin.
Jin area: Modern service industry
Tianjin is among the cities where China’s modern banking industry started and has since developed a mature financial industry base. Tianjin has more than 200 branches of various Chinese and foreign banks, which sets it apart from the rest of the country. This city is also a demonstration area for financial leasing registration. Nankai University, located in Tianjin, was the first institution of higher learning to start offering a financial leasing major in China.
Financial leasing entities are a type of financing institution similar to a bank. Several general and leading financial leasing entities are registered in Tianjin. For example, ICBC Financial Leasing (ICBC), Minsheng Financial Leasing (Minsheng Bank), CITIC Gold Rental (CITIC Bank), Bangyin Gold Rental (Central Plains Bank), Tianyin Gold Rental (Tianjin Bank), etc.
A series of major policy innovations have been implemented in the city, such as the registration of the ownership of leased properties, foreign currency payment for sale and leaseback items, and the facilitation of foreign debts of foreign-funded financial leasing companies. More than a dozen leasing innovations have formed reproducible product and service models and been promoted nationwide. The coverage areas have also expanded from aviation, shipping, marine engineering to high-end automobiles, energy facilities, high-end rail transit equipment, energy conservation and environmental protection, medical services, and infrastructure.
Tianjin’s main development zones
Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area
Tianjin Economic-Technological Development Area (TEDA) was established on December 6, 1984, with the permission of the State Council. As one of the first state-level economic and technological development zones, it benefits from applicable governmental preferential policies aimed at attracting domestic and foreign investment in order to establish high-tech and new-technology-oriented modern industries.
More than 3,300 foreign-invested enterprises have settled in TEDA with a total investment of more than US$ 15 billion. Represented by multinational companies, such as Nestlé, SEW, and Novo Nordisk, it has formed four pillar industries: electronic communications, food, machinery, and biomedicine.
Tianjin Export Processing Zone
The Tianjin Export Processing Zone is one of the first 15 export processing zones approved by the State Council on April 27, 2000. This is a specific enclosed zone where Customs administers items carried into and out of the zone, as well as pertinent locations, 24 hours a day, seven days a week. The central government provided this special economic zone with specific favorable policies to entice processing and trade businesses to operate in the zone. As the center of the Bohai Rim Economic Circle, the geographical location of the Tianjin Export Processing Zone is of strategic significance. Settled in the Tianjin Export Processing Zone, the raw materials imported by the company can easily and quickly enter the export processing zone, and the products produced can be easily transported to foreign markets. The business directory includes Isetan Department Store Co., Ltd., Midland Steel Building System (Tianjin) Co., Ltd.,Tianjin Binhai Sanyo Elevator Co., Ltd. and so on.
Tianjin Port Bonded Zone
The Tianjin Port Bonded Zone was officially established on May 12, 1991, with the approval of the State Council. It is the first free bonded zone in northern China that meets the requirements of modern international economic development. The Tianjin Port Bonded Zone’s international cargo distribution function, commodity exhibition function, as well as financial, foreign exchange, insurance, information, and other service functions are becoming steadily more efficient. A good investment environment and full-service system has been established, attracting more and more domestic and foreign merchants to invest in the zone’s property. Tianjin Port Bonded Zone has attracted a number of multinational companies, such as Merrill Lynch from the United States, Magna from Canada, Philips from the Netherlands, Famous from Switzerland, Kawasaki and Toyota Tsusho from Japan, etc. Industrial clusters, such as electronic information, biopharmaceuticals, machinery and auto parts, metal products, high-tech textiles, and green food, have been formed.
China (Tianjin) Pilot Free Trade Zone
The Tianjin Pilot Free Trade Zone is the first pilot free trade zone in northern China approved by the State Council and is located within the jurisdiction of the Binhai New Area. It officially opened on April 21, 2015. It is an important node of “One Belt and One Road” that has the largest port in the north and the second largest air cargo base in North China. It has opened a China-Europe freight train and realized the efficient connection of Asia-Europe transportation channels. The gathering of trade, investment, and financing businesses is an important platform for China to opening up. Internationally renowned aviation companies, such as Airbus and Lufthansa, have gathered in the area, and it has become an important aviation manufacturing and maintenance base in the Asia-Pacific region.
Tianjin’s efforts in improving its business environment
The Tianjin Municipal Party Committee and the Tianjin Municipal Government have attached great importance to the introduction of foreign investment. They issued a series of policies to encourage foreign investment, which created a good environment for foreign capital to enter Tianjin.
In this regard, foreign investment in Tianjin benefits from relevant national policies and regulations and local foreign investment policies issued by the Tianjin authorities. Local supportive policy goals include:
- Implement the financial industry opening policy: relax restrictions on foreign-funded banking business.
- Optimize foreign investment policies in the automotive sector: ensure that domestic and foreign auto manufacturers produce new energy vehicles enjoy the same market access treatment.
- Optimize scientific and technological innovation services for foreign-invested enterprises: insist that domestic and foreign enterprises are treated equally and encourage and support foreign-funded enterprises to apply for high and new technology enterprise status.
- Strengthen policy publicity and interpretation: make full use of government and departmental portals, “Policy One-Touch” service platform and other channels to make sure the policies released are accessible to the vast majority.
- Reduce the cost of using capital across borders of funds: support foreign-invested enterprises in the Tianjin Pilot Free Trade Zone to handle cross-border RMB receipts and payments through Free Trade (FT) accounts. The FT account is an account with the integration of local currency and foreign currency opened in the FTZ, which can help enterprise achieve convenient conversion between RMB and foreign exchange in this single account, without the need of opening other foreign exchange accounts.
- Make it more convenient for expatriates working in China: relax the age requirements for foreign talents who come to Tianjin to invest and optimize the process of work permits application.
- Optimize the approval procedures for land use application for foreign-funded projects: simplify the application approval materials and shorten the approval time.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article 2022 Import-Export Taxes and Duties in China
- Next Article China’s Market Regulator Drafts New Regulations for Online Advertising