Investing in Zhongshan: Economic Data, Major Industries, and Incentives
Zhongshan, a city in China’s southern Guangdong Province is turning into a major transport hub and crucial driver for the development of the Greater Bay Area. With several major infrastructure projects underway and a host of incentive policies in place, Zhongshan is set to become a strategic hyper-connected investment base from which to tap into the region’s vibrant markets.
China’s Greater Bay Area (GBA) is home to some of the country’s richest cities, namely, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Hong Kong.
However, since there are 11 cities in the GBA all of which are worth our time and attention, we have decided to talk about a rising star within the region. Zhongshan, which besides offering a business environment that is more cost-competitive and investor-friendly than its richer neighbors, is also drawing the attention of the local and international community due to its rapid transformation and growing role within the GBA.
Many people living outside mainland China may not be familiar with the city of Zhongshan, but as the birthplace of Sun Yat-sen, the founding father of modern China, the city has long held an important place in China’s cultural fabric and is now keen on taking its place as a leading urban center in the country’s ambitious Greater Bay Area development plan.
Zhongshan in ancient times was called Xiangshan (literally ‘Fragrant Mountain), a reference to the many flowers that grew around the city. When Sun Yat-sen died on March 12, 1925, the city was renamed as Zhongshan in memory of its most famous son and the country’s most fabled leader (‘Zhongshan’ was one of his most popular names).
Zhongshan 2020 economic profile
Zhongshan reported a GDP of RMB 315.2 billion in 2020 (US$49 billion), a growth rate of 1.5 percent year-on-year. This marks a slowdown from the previous year, which recorded a year-on-year growth of 2 percent. Figures from the first half of 2021 indicate there could be a return to pre-pandemic figures, as the city recorded an annual average growth rate of 4.3 percent since 2019, although growth rates have been falling steadily for several years.
The figure below shows Zhongshan’s steadily growing GDP in the last five years.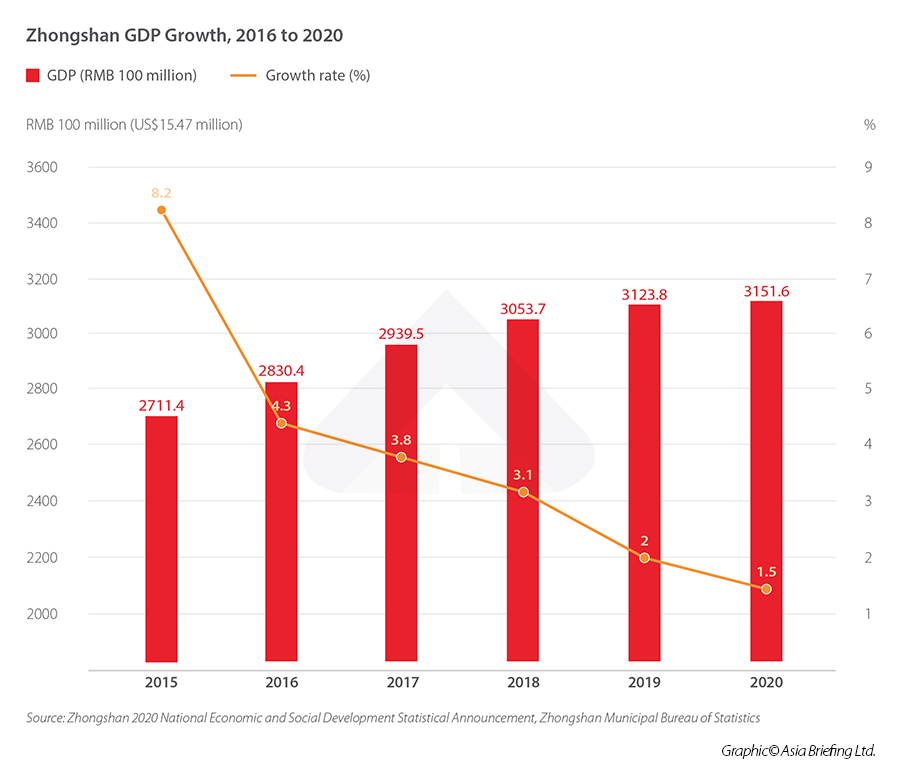
Secondary industries were the largest contributor to the city’s GDP in 2020, making up 49.4 percent of the total. However, primary industries, despite making up just 2.3 percent of the total GDP, saw the highest growth rate in 2020 at 17.5 percent, largely driven by considerable increases in outputs of grain (23.9 percent year-on-year growth), as well as poultry (40.7 percent) and fruits (13.1 percent). This trend has continued into 2021, with data from the first half of the year reporting a 35.7 percent increase in primary industries.
Tertiary industries are closing the gap with manufacturing industries, making up 48.3 percent of the total GDP.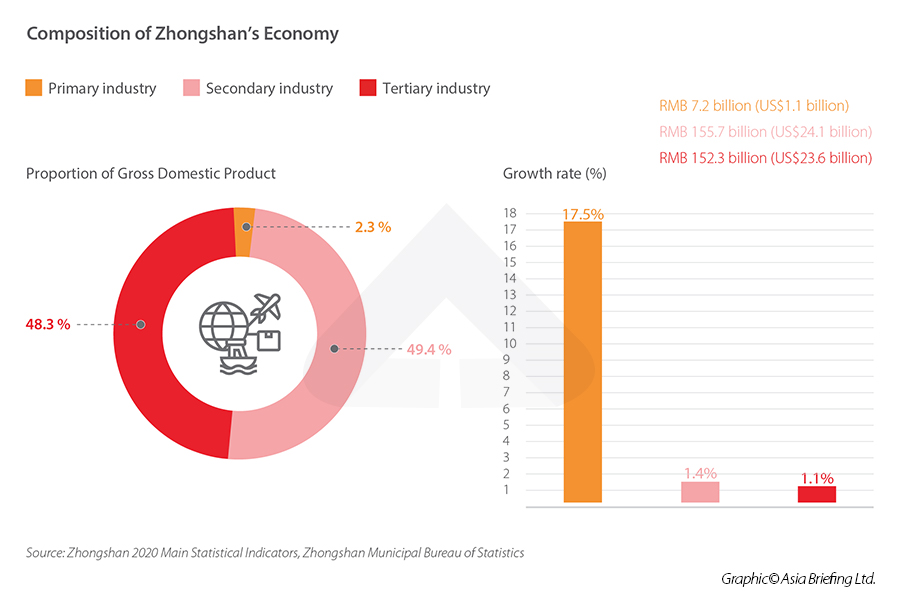
Imports and exports took a significant hit in 2020, with the total volume of import-export decreasing 7.4 percent to reach RMB 220.9 billion (US$34.2 billion). Of this, imports saw the biggest drop, accumulating RMB 39.4 billion (US$6.1 billion), down 14 percent year-on-year, while exports reached RMB 181.5 billion (US$28.1 billion), down 5.9 percent year-on-year.
Despite these downturns, a breakdown of the quarter-by-quarter growth rates showed signs of recovery by the end of 2020, with the overall rate of decline narrowing by five percentage points compared to the first three quarters of 2020.
Actual use of foreign capital, on the other hand, took an unexpected upturn, increasing 9.6 percent year-on-year at RMB 4.05 billion (US$627.6 million). This is in contrast to the trends we have seen in other cities, such as fellow GBA cities Foshan and Dongguan, who suffered from significant drops in foreign investment during the pandemic.
Zhongshan as the GBA’s central transportation hub
Zhongshan sits at the center of the GBA, a region straddling southern China’s Pearl River Delta (PRD). The central government plans to transform this area into an integrated 11-city urban cluster to power the nation’s economic growth.
The city, despite a slowdown in economic growth in recent years, is still on an upward trajectory and is transforming itself into a transport hub for the region, leveraging its central geographical location within the GBA and close links to Hong Kong and Macao.
To realize this vision, the GBA has begun construction on several major transport infrastructure projects in the area. One such project is the Shenzhen-Zhongshan Bridge. Also called the Shenzhong Link, this 24 km sea crossing will connect Zhongshan with the city of Shenzhen on the eastern banks of the PRD. It will consist of a series of bridges and tunnels, starting from Bao’an International Airport on the Shenzhen side. The Shenzhong Link began construction in 2017 and is expected to open to public traffic in 2024.
Other ongoing projects include the Zhongkai Expressway, a 152.5 km road linking Zhongshan with the city of Kaiping to the west, slated for completion in 2023. The Eastern Outer Ring Expressway, set to open along with the Shenzhong Link in 2024, is a 52 km ring road in the east of the city that will serve as a distributor road to the sea crossing and connect with the Zhongkai Expressway.
These transportation advantages will make it much easier to access key transport hubs in the future, reducing travel time to Guangzhou Baiyun Airport, Shenzhen Bao’an Airport, Hong Kong Airport, Macao Airport, and Zhuhai Jinwan Airport to under one hour.
In addition to these newly developed zones and districts, Shiqi Subdistrict, a central urban area of Zhongshan, has built the main passenger transportation hub of the west bank, Zhongshan North Station, which will connect with the Shenzhen–Zhanjiang High-Speed Railway and the Shenzhong Link in the future.
Key industries in Zhongshan city
Currently, Zhongshan serves as a base for advanced manufacturing and modern service industries.
The main sectors of Zhongshan’s industrial clusters are equipment manufacturing, household appliances, textiles and garments, electronics, lighting, healthcare and pharmaceuticals, furniture, and small home appliances and hardware products, as well as emerging industries such as modern services and yachts.
The port area equipment manufacturing base hosts many large-scale state-owned enterprises, such as China Shipbuilding Industry Corporation, China Railway Group Limited, China National Offshore Oil Corporation, and SINOCONST. The only bonded logistics center on the west bank of the Pearl River Estuary is located in Zhongshan.
Prioritized industries in the area include healthcare and medicine, high-end equipment manufacturing, finance, tourism, and exhibitions and conferences.
Zhongshan also aims to grow its manufacturing capabilities and become a forerunner in advanced manufacturing in the country. The subdistrict of Guzhen already hosts some of the finest lighting companies in the world, earning it the nickname ‘China’s lighting capital’.
Many famous international companies have set up presences in Zhongshan, including ThyssenKrupp, ABB, Novartis, ITOCHU, Wistron, Canon, and Foxconn, among others.
Incentive policies for investment and trade
In June of this year, Zhongshan released a whitelist of priority industry clusters deemed strategically important to the region. These include high-end equipment manufacturing, modern light and textiles, intelligent household appliances, next-gen information technology, biomedicine and healthcare, automobiles, and new energy. Investors wishing to set up a business in one of these sectors will be able to enjoy rewards, subsidies, and other advantageous investment conditions.
Zhongshan also enjoys a strong position as an exporting city, and the Zhongshan Taxation Bureau has actively implemented a series of export drawback policies to facilitate the export of “made in China” products. Data shows that from January to May this year, Zhongshan’s export tax rebates reached RMB 7.5 billion (US$1.2 billion), up 49 percent, which collectively benefitted 11,000 export enterprises.
Despite its advantageous position, Zhongshan has long struggled with a shortage of high-end talent, in particular in high-tech industries, often being out-competed by larger and more alluring neighbors, such as Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Hong Kong. To remedy this talent shortage, the city has ramped up incentive policies to attract new high-skilled talent and encourage companies to upskill their existing personnel.
In June of this year, the Zhongshan Science and Technology Bureau government announced the following incentives for upskilling talent:
- Up to RMB 200,000 (US$30,953) in grants for high-tech enterprises who fulfill certain investment requirements to upskill and improve academic qualifications and professional titles of staff for talent that are in short supply.
- 50 percent subsidy of reward programs for talent tackling key technological issues, capped at RMB 500,00 (US$77,344) per year per program and RMB 1 million (US$154,765) total.
- Funding for leading talent in tech innovation – a maximum of RMB 1 million (US$154,765) for expenses related to the development of scientific research and academic seminars. This is available for employers who hire certain high-level talent to establish teams to carry out exploratory basic research and application-oriented technology development in key industries or public fields.
Zhongshan is also one of nine cities in Guangdong Province to provide incentives for foreign talent by granting them individual income tax (IIT) subsidies. The Guangdong IIT subsidy amounts to the portion of the IIT paid by the qualifying overseas talent to the tax bureaus of the nine Guangdong cities in excess of 15 percent of one’s taxable income. The excess portion calculated based on last year’s taxable income can be returned to the talent as a financial subsidy in the current year.
Major development zones in Zhongshan city
As our readers are likely aware, China promotes and differentiates each of its cities to investors by highlighting its strengths in different industries, often by creating parks and special development zones with preferential policies to cultivate these industries.
Zhongshan is no exception, and the city is home to two main development areas, under which there are numerous industrial clusters and development bases.
Below we provide an overview of the two most significant development zones in the city.
Zhongshan Torch High-Tech Industrial Development Zone
The Zhongshan Torch High Tech Industrial Development Zone (ZTHIDZ or ‘the zone’), jointly established by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Guangdong Provincial Government, and Zhongshan Municipal Government in 1990, is the city’s oldest industrial development zone.
This 70 sq km area is home to 250,000 permanent residents and has attracted 430 foreign-invested enterprises, including 20 Fortune 500 companies. Companies, such as Novartis, Canon, and Casio, have established presences within the zone.
The zone has fostered the creation of nine national-level industrial bases as well as industrial clusters for industrie, such as healthcare and pharmaceuticals, intelligent equipment, electronic information, new energy, auto parts, new materials, energy conservation, and environmental protection.
The ZTHIDZ is strategically located at the heart of the GBA transportation hub, with its proximity to Guangzhou Railway Station and Zhongshan North Station providing high-speed rail links to all major cities in China.
The zone is also connected to the region’s dense network of expressways via a number of coastal highways, providing speedy access to the rest of the GBA cities as well as key transport hubs, such as Shenzhen Bao’an International Airport, Guangzhou Baiyun International Airport, Zhuhai Jinwan Airport, and Hong Kong International Airport.
The ZTHIDZ provides support for companies establishing in the area, offering incentive policies for areas like science and technology, finance, R&D, technological transformation, and talent.
The main investment areas encouraged in the zone are advanced equipment manufacturing, healthcare technology, optoelectronic information, and modern services industries – for which subsidies for opening, technological transformation, scientific research, and rent are provided.
Moreover, the investment costs in Zhongshan are much lower than those in Shenzhen or Guangzhou and the zone enjoys close proximity to Hong Kong and Macao.
Other important areas include the Port of Zhongshan, which is a natural estuary port that opens into the PRD, flowing into the South China Sea. It is one of China’s major seaports, primarily handling sea transportation for bulk cargo and containers to Hong Kong, as well as the Chinese coastal region.
It is a small port, but its importance and potential within the GBA is considerable for companies that plan on localizing their productions and shipping to Zhongshan.
Cuiheng New Area
Established in 2013, the Cuiheng New Area (‘Cuiheng’) spans a total planned area of 230 sq km, of which the initial area, composing the island of Ma’an, covers 35 sq km of land and 21 sq km of sea. Cuiheng is conveniently situated to become an important nodal area of the PRD, with the bridgehead of the upcoming Shenzhong Link located on its shores – giving the area a direct land passage to the eastern bank of the PRD. The Zhongshan Hong Kong Macao Ferry Terminal, situated on Ma’an island, links Cuiheng directly to the two namesake economic powerhouses by sea.
The services sector is the main driving force of Cuiheng’s economy, accounting for over 60 percent of the area’s GDP in 2020, above the city-wide 48.3 percent. The Zhongshan Municipal Government has set the goal of pushing this up to 70 percent by 2035, with a key focus on modern services, such as finance and business, technology, conferences and exhibitions, and industrial design.
Cuiheng offers generous incentives to encourage the setting up of company headquarters. Companies that fulfill specific requirements can be rewarded RMB 2 million (US$309,530) to establish headquarters within the area. In subsequent years, companies can receive rewards of up to 50 percent of their financial contribution to the local economy, depending on the industry they are in, capped at RMB 100 million (US$15.48 million).
Companies that are designated as Guangdong’s top 100 private enterprises, the top 500 Chinese manufacturing or service companies, the top 500 Chinese companies, and Fortune 500 companies, can receive rewards of RMB 1 million (US$154,765), RMB 2 million (US$309,530), RMB 3 million (US$464 067), and RMB 5 million (US$773,445) in rewards, respectively.
In step with Zhongshan’s overall development strategy, Cuiheng is also keen to attract and retain top-level talent to the air. To this end, Cuiheng, in cooperation with the Zhongshan Municipal Government, has issued an extensive list of incentives on offer for individuals, research teams, and companies that meet certain eligibility requirements. The incentives include:
- Homebuying subsidies of up to RMB 6 million (US$928,590) total.
- Housing subsidies of up to RMB 6,000 (US$928.59) per month.
- Funding subsidies for establishing ‘academician workstations’ of up to RMB 1.5 million (US$232,147).
- Work funding and living allowance for doctoral and post-doctoral talent of up to RMB 200,000 (US$30,953) per year for a period of two years.
- Rewards of up to RMB 1 million (US$154,765) for companies who successfully hire Tier A and Tier B top-level talent.
A springboard to investing in the GBA
Zhongshan, like many other small cities in the GBA, is a city that has yet to achieve its full potential. It is set to become an integral node in one of China’s most economically vibrant areas and will continue to benefit from the GBA’s ever-growing network of transport links, providing speedy access to the 10 other GBA cities and beyond.
With average labor and living costs that are much lower than elsewhere in the GBA, but with the benefit of easy access to the megalopolises of Shenzhen and Guangzhou, Zhongshan will look increasingly attractive to both investors and workers seeking to develop in the area. Incentive policies for both companies and high-level talent, as well as constantly improving transport infrastructure, is likely to boost this trend.
With the impending implementation of new construction projects in the region and expanding development areas, the near future looks bright for Zhongshan, and it is likely to become even more attractive as an investment destination, a place to work and do business, or simply as a tourist destination.
For investment advice and information on doing business in Zhongshan, please contact Dezan Shira & Associates at zhongshan@dezshira.com.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article What is BEPS 2.0? OECD’s Two-Pillar Plan and Possible Impact on Multinational Enterprises
- Next Article China Removes Didi from App Stores: What We Learned from the Case and China’s Cybersecurity Regime









