China Industries to Watch in 2024
We pinpoint the leading industries in China for 2024, considering their foreign investment outlook, technology transformation, market prospects, and supportive government policies.
In the dynamic landscape of China’s industries, 2024 promises notable growth and transformation across various sectors. From the resilience of the fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) market to the revolutionary shifts in education and healthcare, each industry showcases distinctive trends and opportunities for foreign investment. In this article, we look into the Chinese industries and sectors most likely to experience fast-paced growth in 2024.
Education
The education industry in China continues to be a significant and rapidly growing sector, maintaining its status as a crucial component of the country’s economic and social development.
Anticipated to experience a robust annual growth (CAGR) of 8.73 percent from 2022 to 2027, the market volume is poised to reach a noteworthy US$2.32 billion by the year 2027.
Education technology and digital learning remain high-potential markets
As China continues to invest substantially in education and the industry projects robust growth, the education technology (EdTech) sector in 2024 becomes a focal point for foreign companies, offering an array of opportunities to leverage emerging trends and technologies.
In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the landscape of education in China underwent a transformative shift, particularly within the growing Edtech sector. Originally considered a contingency plan in December 2019, online teaching rapidly evolved into the “new normal” as classrooms transitioned into virtual spaces. The strict shelter-at-home policies enforced during the quarantine period not only propelled online education to the forefront but also catalyzed a remarkable surge in demand within China’s EdTech market.
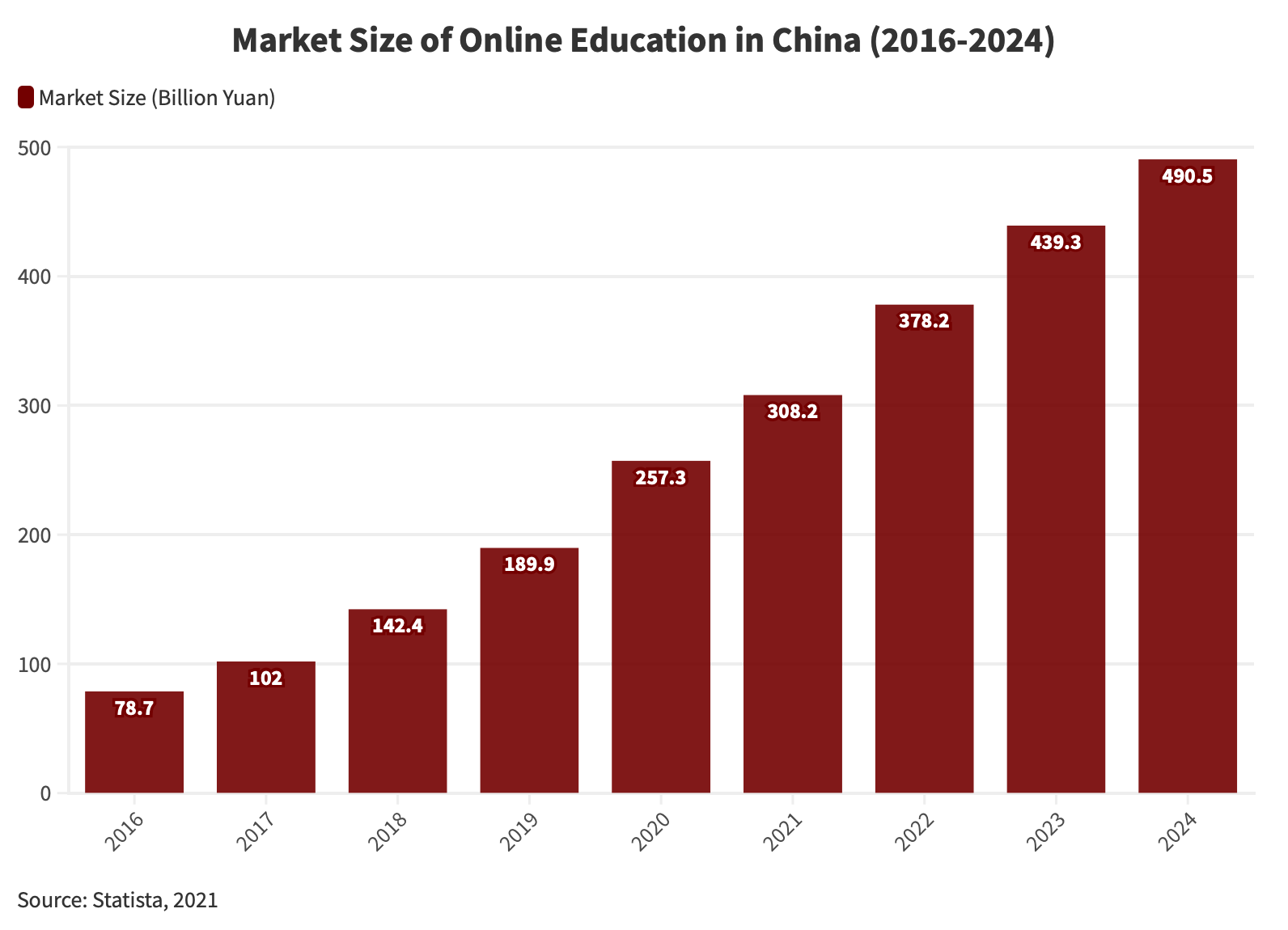 Against the backdrop, the EdTech sector emerged as one of the country’s fastest-growing domains. Remarkably, in 2020, the market size of China’s online education industry reached an impressive RMB 257.3 billion (US$36.2 billion), marking a substantial 35.5 percent increase from the previous year, and showcasing the resilience and adaptability of the education landscape in response to unprecedented challenges.
Against the backdrop, the EdTech sector emerged as one of the country’s fastest-growing domains. Remarkably, in 2020, the market size of China’s online education industry reached an impressive RMB 257.3 billion (US$36.2 billion), marking a substantial 35.5 percent increase from the previous year, and showcasing the resilience and adaptability of the education landscape in response to unprecedented challenges.
Driven by the government’s substantial investment in education and the projected industry growth rate, China’s EdTech sector presents lucrative opportunities for foreign companies. They can benefit from emerging trends and technologies such as:
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI-powered adaptive learning platforms and intelligent tutoring systems are gaining traction, providing personalized learning experiences that resonate with Chinese students.
- Virtual reality (VR): The application of VR technology in creating immersive learning experiences is on the rise. From medical training to practical simulations, VR offers unique opportunities for educational innovation.
- Mobile learning: With an enormous user base of over 1 billion mobile phone users, mobile learning is a thriving trend. E-learning platforms are adapting by developing mobile apps, enabling learners to access educational content on the go.
- Social learning: Leveraging social media platforms for social learning is a growing trend. Connecting learners with peers and experts globally fosters collaborative learning environments.
- Gamification: Incorporating gaming elements into educational software enhances engagement and interactivity. This approach makes learning more enjoyable and effective for students.
Vocational training sector
While certain sectors within China’s education industry, notably private tutoring, have been specifically impacted by government reforms, the current policy landscape in China suggests a favorable environment for investment in vocational education.
China’s vocational training industry exhibited a sustained CAGR of 8 percent between 2017 and 2022 and is now projected to reach a market volume of RMB 909.7 billion (US$125.99 billion) by 2026.
The Chinese government has created a favorable climate to invite foreign direct investment (FDI) into the vocational training industry. The latest Special Administrative Measures (Negative List) for Foreign Investment Market Access (hereinafter, National Negative List) and the Special Administrative Measures (Negative List) for Foreign Investment Market Access to Pilot Free Trade Zones (hereinafter, FTZ Negative List), stipulated different market entry requirements for FDI in the sector.
In addition, China has pilot programs in certain cities to facilitate the market entry of foreign-invested vocational training businesses. In Beijing and Shanghai, for example, regulations were recently introduced providing scope for-profit foreign-invested vocational training institutions.
To learn more about opportunities in China’s vocational training industry, read our article here.
Government support policies and tax incentives
In June 2023, the State Taxation Administration (STA) released the Guidance on Preferential Tax Policies to Support the Development of Education, which underscores the commitment to fostering growth within the broader education landscape. Comprising 28 tailored tax policies, these incentives play a pivotal role in enhancing various facets of the education industry, creating an enabling environment for domestic and foreign businesses alike.
Key government incentives include:
- Tax incentives for educational and teaching activities: Noteworthy tax exemptions on value-added tax (VAT) for academic schools, Sino-foreign cooperative schools, and vocational school-affiliated enterprises align with the government’s drive for diverse education models and innovative teaching methodologies.
- Tax incentives reducing operating costs: Exemptions from property tax, urban and township land use tax, and deed tax for specific educational institutions play a crucial role in cost management. This allows educational entities, including schools, nurseries, and kindergartens, to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring a sustainable educational landscape.
- Tax incentives encouraging social contribution: Deductions for educational donations, stamp tax exemptions for property transfers to schools, and incentives for vocational education investment reflect the government’s dedication to involving social forces in the educational realm. Beyond attracting private investment, these measures promote corporate social responsibility in supporting the broader educational sector.
For a comprehensive list of the new incentives, please refer to this article.
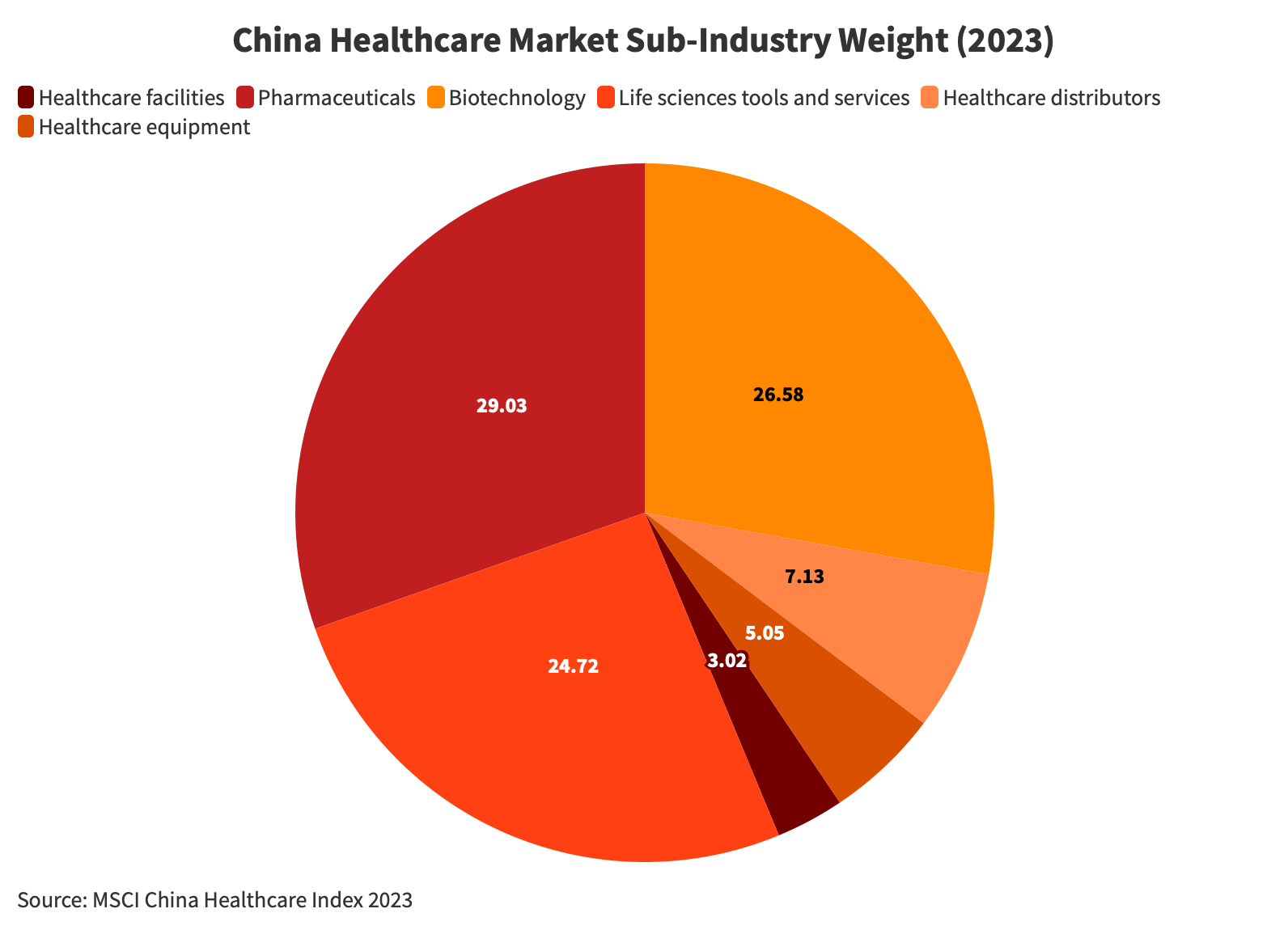
Healthcare
China’s healthcare industry stands as a colossal and diverse sector, catering to a population exceeding 1.4 billion people. The demand for healthcare services is substantial, driven by an aging population and lifestyle changes, resulting in a surge of chronic diseases across all age groups.
Notably, China’s healthcare market is predicted to expand from around US$900 billion (RMB 6.47 trillion) in 2019 to US$2.3 trillion (RMB 16.53 trillion) in 2030, and its market size is second to only the US.
Technological advancements and digital healthcare
The digital health market in China is set to exhibit an impressive CAGR of 12.37 percent from 2023 to 2028. This trajectory foresees substantial expansion, culminating in a projected market volume of US$82.72 billion by 2028. The country’s progressive integration of digital solutions and simultaneous technological breakthroughs in medical devices position this sector as a focal point for innovation and growth in 2024.
In global comparison, China stands out as the frontrunner, expected to generate the most revenue in the digital health market in 2023, reaching US$46,170.00 million. This dominance reflects the country’s progressive approach to integrating digital solutions into its healthcare ecosystem.
In tandem with the digital healthcare evolution, China has also experienced a surge in technological innovations within the realm of medical devices. Breakthroughs in diagnostics, monitoring, and treatment have been propelled by developments such as wearable health devices, remote monitoring tools, and advanced imaging systems.
Eldercare and childcare services
As China grapples with the demographic shift brought about by an aging population, the demand for eldercare services has seen a noteworthy upswing. China’s eldercare market is predicted to reach US$800 billion by 2025 and to exceed US$3 trillion by 2030. This underscores the profound economic and societal implications of the eldercare sector, positioning it as a pivotal component of China’s evolving healthcare landscape.
With strategic government support and comprehensive measures, the eldercare and childcare service industries are poised for growth in 2024, addressing both economic challenges and societal needs.
Recognizing the urgency of addressing the challenges posed by demographic shifts, the Chinese government has prioritized support for eldercare and childcare services. In 2022, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) unveiled a comprehensive set of measures. These initiatives are strategically crafted to provide robust support to the eldercare and childcare service industries, with a primary goal of alleviating economic hardships faced by businesses integral to the social fabric of the nation.
Biopharmaceuticals
Benefiting from a robust manufacturing base, the biopharmaceutical industry in China is increasingly aligning with international standards. In particular, the innovation ecosystem within China’s biopharma sector has witnessed rapid evolution since 2015, marked by advancements in regulatory compliance, enhanced funding levels on par with global standards, and active engagement in cross-border partnerships and transactions.
As of today, China’s biopharma segment is poised for remarkable growth, and its market volume is expected to surge from RMB 345.7 billion (US$47.60 billion) in 2020 to an impressive RMB 811.6 billion (US$111.76 billion) by 2025. This signifies a staggering 135 percent increase within a span of five years.
FMCG
China’s FMCG market has navigated challenges in recent years, notably the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a considerable slowdown in growth. The pre-pandemic robust annual growth rate of over 5 percent in 2019 experienced a drastic reduction by 2022.
However, against this backdrop of adversity, the sector exhibited remarkable resilience, staging a rebound since the fourth quarter of 2022, and remains one of the sectors worth monitoring in the coming year. The last three years have witnessed slower low-value sales, a consequence primarily attributed to the surge in COVID infections. The ensuing implementation of restrictions on mobility and consumer spending created a ripple effect.
FMCG segments to consider for sustained growth in 2024
- Food and beverage: After a strong performance in 2022 due to increased at-home consumption, certain segments like instant noodles, soft drinks, and frozen food may experience slower growth in 2023 and 2024 as out-of-home dining resumes. However, staples like herbs, spices, and cooking oils are expected to maintain growth, reflecting the continued trend of home cooking habits established during the pandemic. For a complete overview to exporting food products to China, consult our updated guide.
- Household care: Despite a gradual slowdown from 2020 to 2022, the household care sector is expected to perform well in the next two years. As consumer confidence improves, there may be a shift towards premium products with added sanitization benefits, driving growth in this category.
- Cosmetics and personal care: After facing challenges during the pandemic, particularly in skincare and cosmetics, the cosmetics and personal care sector is anticipated to achieve a robust growth rate of 4-6 percent in the post-COVID era, with a projected market expansion to US$78 billion by 2025.
Clean energy
In 2024, China’s clean energy sector is set for substantial growth, leading globally in renewables. Reuters reports of China’s record-breaking installation of 230 gigawatts (GW) in wind and solar power, more than what the United States and Europe combined are expected to achieve.
Simultaneously, the country is investing heavily in related projects, with an estimated expenditure of US$140 billion in 2023. China has increased its 2025 wind and solar outlook by an impressive 43 percent (380 GW) in just a few years, setting it apart from some other markets that are scaling back their renewables targets.
These findings position China as a central player in the global clean energy transition. With over 80 percent of the world’s solar manufacturing capacity expected to be in China through 2026 and the ability to meet a substantial part of the global demand for the next decade, China’s clean energy sector remains a key industry to watch in 2024.
In addition to its impressive domestic growth in the clean energy sector, China is actively promoting foreign investment in renewable energy and related sectors. The government is making concerted efforts to attract foreign investors to participate in both upstream and downstream activities, fostering an environment conducive to international collaboration in the renewables industry.
Key sectors in the renewable energy space that are specifically encouraged for foreign investment include:
- Construction and operation of new energy power stations: Encompassing solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, tidal energy, current energy, wave energy, and biomass energy.
- Construction and operation of regional energy supply projects: Focused on cold and heat, driven by renewable energy resources.
- Construction and operation of biogas projects: Highlighting the potential for foreign investment in sustainable biogas initiatives.
- Manufacturing of new energy power generation equipment: Covering the production of set or key equipment for new energy power generation.
- Development and application of complementary systems: Specifically for power generation utilizing gas and renewable resources.
- Research and development (R&D) and application in large energy-storage technologies: This includes thermal battery, pumped storage technology, air energy storage technology, and innovations in wind power and heating after midnight.
New energy vehicles
Currently possessing more than half of the world’s electric cars, and having already exceeded its 2025 target for new energy vehicles (NEVs) sales, China is a global leader in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. To further boost domestic sales in this sector, the government announced an extension of its tax exemption policy for NEVs until 2027. This extension directly benefits consumers by reducing costs associated with purchasing NEVs, thereby anticipated to generate strong support and interest in the EV market.
Further, as the adoption of electric vehicles rises, the necessity for batteries and their key components, including lithium, nickel, and cobalt, will grow. This increased demand for upstream battery raw materials is poised to have a cascading effect on related industries, encompassing mining, refining, and manufacturing.
All in all, the extension of China’s tax exemption policy for NEVs, coupled with its global leadership, consumer incentives, and the anticipated surge in demand for battery raw materials, makes the EV sector a compelling investment opportunity for foreign businesses and investors in 2024.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the outlook for China’s industries in 2024 is marked by dynamic growth and transformative trends, offering diverse opportunities for international investors and businesses. Growth with a focus on sustainability is expected to resound across major world markets including China. The convergence of government policies with the need for greater foreign investment, sustainable industrial transformation, changing consumer needs, and global cooperation thus positions China as a key economic player and investment base in 2024.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, Dubai (UAE), and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China’s Economy in 2023 – A Year of Growth and Recovery
- Next Article Chinas Wirtschaft im Jahr 2023 – Wachstums und Erholung