Foreign investment in China can be made through a variety of investment vehicles. The best investment structure for your business is determined by a variety of factors, including its planned activities, industry, and investment size.
In this section, we discuss the following entity types, their registered capital requirements, timeline for setting up, and key HR positions:
- Representative Office (RO);
- Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE);
- Foreign Invested Commercial Enterprise (FICE)
- Joint Venture (JV); and
- Foreign Invested Partnership (FIP).
Setting up a Representative Office ("RO")
An RO is an attractive way for foreign investors to become accustomed with the Chinese market as it is the easiest type of foreign investment structure to set up. An RO is an extension of the foreign company without independent legal personality, unlike more robust vehicles, such as the WFOE. When an RO signs a contract, it is the foreign company that is bound by the agreement.
There are only a limited number of activities an RO is permitted to be engaged in. ROs are forbidden from engaging in any profit-seeking activities and may only be used to facilitate the activities of the foreign company in China. These are:
- Market research, display, and publicity activities that relate to company products or services; and,
- Liaison activities that relate to product sales or services and domestic procurement.
An RO cannot directly hire Chinese employees. Instead, it is required to employ local staff through a qualified labor dispatch agency. The agency acts as the employer for legal purposes and sends employees to work at the RO for a fee. An RO may directly hire up to four foreign nationals as the representatives who do not need to go through the agency.
Even though an RO does not earn revenue, it is still subject to Chinese tax. ROs are taxed as a permanent establishment in China, which usually amounts to a liability of approximately eight percent of the total expenses of the RO.
RO is a beneficial option for companies that are procuring from China and want to keep staff on the ground for quality control, or for maintaining short communication lines with China-based suppliers, agents, and distributors.
Requirements and registered capital
An RO doesn’t need registered capital to operate in China.
Time to establish
To set up an RO, the overseas parent company must have already been in existence for two years.
- Obtain notarized & legalized documents and requisite certificates – 01 month.
- Set up necessary accounts & chops – 1-2 months.
- Total time – at least 2 months.
Key positions in an RO
ROs should designate a chief representative to sign documents on behalf of the company. In addition to a chief representative, an RO can also nominate three more general representatives.
Setting up a Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise ("WFOE")
A WFOE is a limited liability corporation with a relatively simple management structure that is entirely owned by one or more foreign investors.
A WFOE can make profits and issue local invoices in RMB to its suppliers, unlike an RO. A WFOE can employ local staff directly, without any obligations to employ the services of an employment agency. It can also expand to create subsidiaries in China.
If compared to a JV, a WFOE has better autonomy and flexibility to execute the company policies intended by the investors without considering the Chinese partner. It may also hold certain advantages when protecting the company’s intellectual property and technology.
A WFOE is not feasible if the targeted sector is listed as “restrictive” in the Special Administrative Measures on Access to Foreign Investment ("National Negative List”) or the Free Trade Zone Special Administrative Measures on Access to Foreign Investment (“FTZ Negative List”), where foreign investors need to have a Chinese equity partner to form the business. Incorporating a WFOE to engage in these sectors would not be permitted.
However, the setup procedure of a WFOE is more complicated.
There are three distinct WFOE setups available:
- Service (or consulting) WFOE;
- Trading WFOE (or foreign-invested commercial enterprise [FICE]); and
- Manufacturing.
While all three structures share the same legal identity, they differ significantly in terms of their setup procedures, costs, and the range of commercial activities in which they are allowed to engage. Trading WFOEs and manufacturing WFOEs must derive the majority of their revenue from their manufacturing but can also provide associated services. Service WFOEs can conduct trading activities related to their services.
Requirements and registered capital
There is no minimum capital requirement for a WFOE to operate in China. Every WFOE has a different amount of registered capital, which it must choose based on its operational needs.
Time to establish
Depending on the size of the company, a WFOE can take two to nine months to set up.
Key positions in a WFOE
Shareholders and executive director (or board of directors)
For WFOEs, the shareholders’ meeting is the company’s highest decision-making body, and its resolutions on business matters are implemented by the executive director or the board of directors. For joint ventures established before January 1, 2020—the effective date of the Foreign Investment Law—the board of directors remains the top authority, but these entities are required to adjust their governance structure within the five-year transition period, i.e., by January 1, 2025. For joint ventures formed on or after January 1, 2020, the shareholders’ meeting serves as the highest governing body.
Supervisor(s)
WFOEs are generally required to appoint at least one supervisor to monitor the performance of directors and senior management. For joint ventures, this was not a mandatory requirement prior to the implementation of the Foreign Investment Law. However, from January 1, 2020, newly established JVs must also appoint supervisors in accordance with the Company Law, and JVs formed before that date are required to complete the necessary governance adjustments by January 1, 2025.
Under the New Company Law, limited liability companies may establish an audit committee within the board of directors, in which case a separate board of supervisors (or individual supervisors) is no longer required. The audit committee, composed of board members, may exercise the statutory powers of the supervisors. In addition, small-scale LLCs or companies with a limited number of shareholders may appoint only one supervisor, and with unanimous shareholder approval, they may choose not to appoint a supervisor at all.
General Manager
Both WFOEs and joint ventures are required to appoint a general manager responsible for the company’s daily operations. This role may be held concurrently by the executive director or by a member of the board of directors. In the case of JVs, multiple deputy general managers may also be appointed, and together with the general manager, they are collectively referred to as the management office.
Chief financial officer
The chief financial officer (CFO), or financial employee in charge, is a key personnel of a company who has primary responsibility for managing the company’s finances, including financial planning, finance, and accounting compliance, taxation, cash flow tracking, as well as financial reporting analysis.
The CFO is senior management by nature and reports to the general manager of the company. This position may be concurrently filled by a member of the board of directors. CFO is of special importance in China during the company setup stage, where the CFO needs to go through real name authentication and be the contact person with the authority in charge.
Legal representative
Every business established in China, foreign or domestic, is required to designate a legal representative, i.e., the person responsible for performing the duties and powers on behalf of a company.
Currently, the executive director, the Chairman of the board of directors, or the general manager are eligible to be legal representatives. The 2023 Company Law expands the scope of selection of legal representatives to all directors or managers who carry out affairs on behalf of the company.
Powers and responsibilities of a legal representative
The Company Law does not clearly define the powers of a legal representative. However, a legal representative is authorized to perform all acts of the general administration of a company according to the company’s aims and objectives. This may include:
- Acting (legally) to conserve the company’s assets;
- Executing powers of attorney on the company’s behalf;
- Authorizing legal representation of and litigation by the company; and
- Executing any legal transactions that are within the nature and scope of that company.
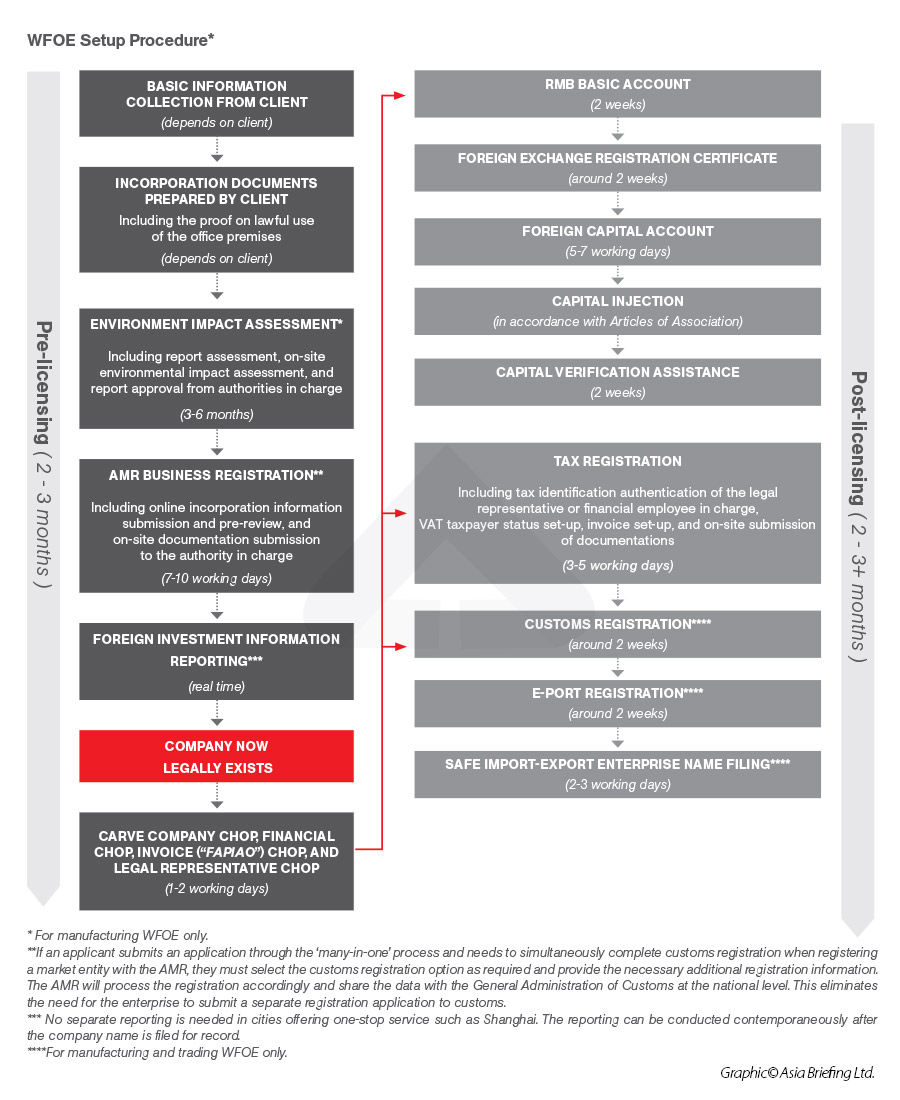
Setting up a Joint Venture ("JV")
A JV is formed by one or more foreign investors, along with one or more Chinese parties. After the enactment of the FIL, Chinese individuals can now become shareholders in a JV, providing greater flexibility in selecting business partners.
There are mainly two reasons for foreign investors to choose a JV structure:
- The foreign investor wants to invest in a restricted industry sector, where the law permits foreign investment only via a JV with a Chinese partner; and
- The foreign investor wants to make use of the sales channels and network of a Chinese partner who has local market knowledge and established contacts.
Before the FIL was enacted, there were two types of JVs in China, and they differ primarily in terms of how profits and losses are distributed:
Equity Joint Venture (EJV):
- Profits and losses are distributed between parties in proportion to their respective equity interests in the EJV;
- The foreign partner should hold at least 25 percent equity interest in the registered capital of the EJV; and
- An EJV should be a limited liability.
Cooperative Joint Venture (CJV):
- Profits and losses are distributed between parties in accordance with the specific provisions of the CJV contract; and
- A CJV can be operated either as a limited liability company or as a non-legal person.
The newly formed JVs are subject to the terms of the Company Law following the implementation of the FIL(2020), which necessitated adjustments in several areas, including governing structure and operational procedures. Read about the impact of Foreign Investment Law on Businesses in China.
JVs created before January 1, 2020, in accordance with the previous EJV Law or CJV Law, are required to make relevant adjustments before January 1, 2025, to comply with the new standards.
Requirements and registered capital
There is no minimum registered capital required for a JV. However, the 2023 Company Law requires that shareholders must pay their subscribed capital within five years from the company’s establishment.
Time to establish
A JV's incorporation takes five to six months.
Key positions in a JV
Same as WFOE.
However, JVs established before January 1, 2020, will need to transition their governing structure by 2025 to the three-tier structure, following the company law. Read more about the new foreign investment law's impact on key positions in FIEs.
Setting up a Foreign Invested Commercial Enterprise ("FICE")
A FICE, which can be set up either as a WFOE or a JV, is a type of company for retail, franchising, or distribution operations. A WFOE or JV can be established exclusively as a FICE, or can combine FICE activities with other business activities, such as manufacturing and services.
FICE is inexpensive to establish and can be of great assistance to foreign investors because it combines sourcing and quality control activities with purchasing and export facilities, thus providing more control and a quicker reaction time compared to sourcing exclusively via an overseas headquarters.
FICEs are also the ideal choice for foreign companies that need to source from China to resell to their domestic consumer market. Without a Chinese trading company, the alternative would be to buy from overseas and have the goods shipped out of China before then reselling them back to China (which would mean additional logistical costs, customs duties, and value-added tax).
Requirements and registered capital
There is no minimum capital requirement for FICE.
Time to establish
A FICE can take four to six months to set up before fully operational.
In some instances, a FICE may require foreign investors to inject capital within a certain period, especially for businesses located in industrial parks and in specific industries.
Other entity options
Foreign Invested Partnership ("FIP")
An FIP can be newly established by foreign investors contributing to the partnership, or formed through the acquisition of equity interests in an existing domestic partnership. By definition, an FIP requires two or more investors to conduct business and is therefore not suitable for foreign investors seeking 100 percent ownership or sole control of an entity. In addition, foreign investors may not use an FIP to enter sectors that are subject to foreign equity restrictions under the Negative Lists.
A partnership is not a separate legal person, but a contractual arrangement between two or more parties conducting business under a common name and registered with the authorities. Unlike companies governed by the Company Law, partnerships offer investors significant flexibility in internal governance arrangements. Profit distribution and voting rights do not need to correspond to capital contributions, allowing partners to structure commercial and control rights more freely.
While the Partnership Enterprise Law provides that, in principle, unanimous consent of all partners is required for the transfer of a partnership interest, partners may agree otherwise in the partnership agreement. As a result, it can be considerably easier to transfer participation interests in an FIP than in a company structure, depending on how the agreement is drafted.
Variable Interest Entity ("VIE")
VIE (Variable Interest Entity) structures are widely used by foreign investors to participate in sectors that are restricted or prohibited to foreign investment under the Negative Lists, such as telecommunications and education.
Under this arrangement, foreign investors maintain de facto control over domestic operating companies through a series of contractual agreements, rather than through direct equity ownership. As a result, investors face the risk that their control could be undermined by intentional breaches of contract or other enforcement challenges, since the structure relies on the continued effectiveness and enforceability of private agreements.
What’s next for VIE’s?
The government’s regulatory stance on VIE structures remains uncertain. The Foreign Investment Law (FIL) does not clearly state whether VIE arrangements are lawful or whether they fall within the statutory definition of “foreign investment.” However, the Implementing Regulations on the Promotion of Private Education (revised in 2021) explicitly prohibit the use of VIE structures in the private education sector, and similar arrangements could be deemed illegal in other sectors that remain closed to foreign investment.
At the same time, the China Securities Regulatory Commission (CSRC) has confirmed that qualified companies using VIE structures may still list on overseas stock exchanges, indicating a degree of regulatory tolerance in the capital markets context. Given these regulatory ambiguities and sector-specific restrictions, foreign investors considering VIE structures are advised to closely monitor policy developments and regulatory enforcement trends before proceeding.
The Foreign Investment Law (FIL) for business entities
The FIL governed foreign investment since January 1, 2020, repealing previous laws on WFOEs, CJVs, and EJVs. FIEs established under old laws must adjust to comply by January 1, 2025, including:
- CJVs no longer exist;
- WFOEs comply with statutory fund reserve rules in the Company Law; and,
- EJVs transition governance to a board of shareholders and the supervisory board, align equity transfer, profit distribution, capital changes, and articles of association with the Company Law.
Foreign investors should finalize these adjustments promptly.
Foreign investment law's impact on key positions in FIEs
Considering that WFOEs are generally limited liability companies, which are basically in line with the Company Law, the FIL has a limited impact on key positions in WFOEs.
For existing FIEs in the form of a CJV or EJV, they need to change their governing structure before January 1, 2025, to the three-tier structure (the board of shareholders, the board of directors, and the general manager), in accordance with the Company Law.
Below, we take EJV as an example.
|
FIL’s Impact on Key Positions in EJV |
||
|
Items |
Under the EJV Law |
Under the new FIL |
|
Highest authority |
Board of directors |
Board of Shareholders or the General Meeting of shareholders |
|
Board of shareholders |
No board of shareholders |
The following matters must be reviewed and approved by shareholders holding two-thirds or more of the voting rights at the shareholders’ meeting:
|
|
Board of directors |
|
|
|
Supervisor |
The board of supervisors/supervisor is not obligatorily required |
|
|
Legal representative |
Chairman |
Chairman, executive director, or general manager |
|
Senior management personnel |
Where the Chinese party takes the position of general manager, the position of the vice-general manager shall be held by the foreign party, and vice versa |
No limitation |
Beneficiary owner filing
Below is Content A updated using Content B, with added legal references, effective dates, penalties, and clarified procedures:
Beneficial Owner Filing
Companies, partnerships, and branches of foreign companies established in China are required to file beneficial owner information through the relevant corporate registration system. Failure to comply may result in administrative penalties of up to RMB 50,000 (approximately US$6,900).
For entities established on or after November 1, 2024, beneficial owner information must be submitted at the time of establishment registration through the online registration system. If online filing is not available, registration may be completed on-site, but beneficial owner information must still be filed within 30 days after establishment.
Entities that were registered before November 1, 2024 must complete their beneficial owner filings by November 1, 2025.
Entities Required to File (Filing Entities)
- Companies
- Partnerships
- Branches of foreign companies
Temporarily Exempt Entities (Based on Current AML Risk Assessment)
- Non-corporate legal persons
- Sole proprietorships
- Farmers’ professional cooperatives (and their federations) and their branches
- Branches of domestic companies and partnerships
This exemption scope may be adjusted in future regulatory updates.
SME Exemption via Commitment Letter
To reduce compliance burdens for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) with simple ownership structures, registered entities may be exempt from ongoing beneficial owner reporting if all of the following conditions are met:
- Registered capital (or investment amount) does not exceed RMB 10 million (or equivalent foreign currency).
- All shareholders or partners are natural persons.
- No individuals other than the shareholders or partners exercise actual control over the entity.
- No control or benefit is exercised through non-equity or non-partnership means.
If these conditions are satisfied, eligible entities may confirm and submit a commitment letter through the registration system to be exempted from further reporting.
If, for example, a person who is not a registered shareholder controls the company through contractual arrangements, the entity would not qualify for the exemption and must file beneficial owner information.
Entities opting for exemption must ensure the accuracy of their declarations. False or misleading commitment statements may lead to legal liability and penalties.
Alternative options
In addition to traditional investment options, foreign investors are actively exploring alternative arrangements to enter the Chinese market at a lower cost and with greater flexibility. This strategic approach aims to adapt to the evolving business landscape.
Overall, an increasing number of foreign investors and businesses are pursuing methods to sell into or source from China while maintaining a minimal on-site team and operational footprint. They rely more on virtual support services to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Some emerging options include:
- Professional employer organization (PEO)’s employer service;
- Exporter of record (EOR) and importer of record (IOR) service;
- Cross-border trade; and,
- Virtual office service.
PEO’s employer service
Traditionally recognized as a form of full-service human resource outsourcing, PEO (Professional Employer Organization) employer services have been utilized by some foreign investors to enter or sustain a presence in the Chinese market.
Under the PEO employer service arrangement, the PEO service provider signs separate contracts with both the foreign company and the employees designated to work for the China investment. While the day-to-day control and working relationship with employees remain with the overseas company and its outsourced hires, the local PEO service provider in China manages payroll and tax filing, benefits administration, compliance, and risk mitigation.
This setup allows foreign companies to benefit from having full-time staff working in overseas markets while staying compliant with local laws, without the time and investment required to establish and operate an overseas establishment. As an entry strategy, it frees up critical resources for the foreign firm to explore options in a new or unfamiliar market. Investors can leverage this arrangement to gain firsthand knowledge of the local business environment and culture, assess market suitability, plan against supply chain disruptions, and establish a sustainable long-term strategy.
For those reconsidering their China strategy and contemplating scaling down their exposure without a complete exit, PEO employer services offer a viable option to maintain a small number of employees on the ground conveniently and at a lower cost.
EOR and IOR service
For foreign investors looking to sell into or source from China, EOR and IOR services have emerged as convenient and secure options for managing export and import processes, eliminating the need for physical representation or a presence in China.
EOR or IOR refers to an authorized person or entity responsible for ensuring the successful export or import of goods. The EOR or IOR is tasked with acquiring necessary export/ import documentation, such as licenses and permits, and their name is included in shipping documentation as the exporter or importer. Additionally, EOR or IOR services encompass:
- Accurately describing and valuing exported/imported goods;
- Ensuring compliance with export/import regulations and securing customs clearance;
- Meeting all financial obligations;
- Being accountable for the release of goods; and
- Maintaining relevant documentation for audits.
While a freight forwarder or customs broker can theoretically serve as the EOR or IOR, they often lack the expertise and resources to perform these tasks.
EOR or IOR becomes particularly essential when foreign investors lack a legal entity in China or possess one without foreign trade registration, necessary licenses or permits, or expertise in local compliance requirements.
Utilizing an EOR or IOR streamlines import/export efforts, mitigates associated risks, and ensures efficient shipment delivery. This approach enables foreign investors to expand their business into the China market without investing significant time and resources in research and development.
Cross-border trade
Cross-border trade is another option utilized by foreign investors to sell into or source from China.
This type of trade involves international commercial activities where entities getting clearance from different countries engage in transactions through e-commerce platforms, conduct electronic payment settlements, and deliver goods through cross-border trade logistics or off site warehousing to complete transactions. Due to the essential role of e-commerce platforms in this arrangement, cross-border trade is commonly referred to as cross-border e-commerce.
In simpler terms, when a foreign investor sells a product from overseas to buyers in China or sources a product from China to a foreign country through cross-border e-commerce platforms, it qualifies as cross-border trade.
China, being the world’s largest e-commerce market, actively promotes cross-border trade by establishing bonded areas and e-commerce pilot zones, facilitating the import and export of goods, and offering attractive tax incentives.
For products sold to Chinese consumers through cross-border trade, transactions valued below RMB 5,000 or total annual e-commerce transactions below RMB 26,000 are exempt from import tariffs and can enjoy a 30 percent value-added tax or consumption tax reduction if applicable.
Moreover, selling directly to Chinese consumers via cross-border trade comes with the advantage of minimal administrative requirements, and in many cases, an online store can be launched within months. In addition to not requiring a legal entity in China, the customs clearance and the labeling requirements might be less stringent compared to general trade, subject to certain qualifications. Many platforms also support merchants by handling administrative affairs like customs registration and clearance procedures.
However, this convenience comes with trade-offs. E-commerce platforms often require relatively large security deposits to manage the risk associated with hosting products from foreign entities. Notably, not all products can be sold via cross-border trade; only those listed in the Cross-Border E-Commerce Retail Import Commodities List (the CBEC Whitelist) can enter China through this mode.
Virtual office service
A virtual office service is another cost-effective option for foreign investors seeking entry into the Chinese market. This service provides businesses with physical address and office-related amenities without the need for long leases or administrative staff hires. The flexibility of month-to-month leasing allows foreign investors to make changes to their business setup as needed.
Additionally, a virtual office typically offers services such as a mailing address, phone answering services, videoconferencing capabilities, and access to meeting rooms when required, creating the appearance of a larger business entity. This setup is particularly popular among startups and small businesses, especially in an era where remote work is increasingly prevalent.
However, the use of a virtual office address for company registration depends on local regulations. While virtual office services are more accessible and widely accepted in larger cities, careful consideration and research are necessary when planning a business structure that involves virtual office services in smaller cities.
Effective pre-planning is crucial for utilizing certain services provided by virtual offices, such as meeting room usage. The potential impact on productivity in a remote work setting is also a consideration for businesses operating in a virtual office environment.











